World History - AP 10th Grade
Patterns of Interaction
|
Teacher: M. Cisneros
Room: A-210 Course: World History Text: World History: Patterns of Interaction The World History course is an academic, yearlong course with a focus on the development of human interaction and the global processes that have shaped history from 1000 B.C.E to the present. In addition to the textbook, students will be engaged through a variety of sources including primary source documents, maps, simulations, plays, debates, videos, lectures, and computer-technology assignments. Remember, it is expected that students come prepared at all times! Furthermore, an important part of learning history is discussing the various aspects of any given topic. Discussions are an open forum for students to express their views in an environment of tolerance, understanding, and honesty. It is expected that all students come to class with open minds, listen to others, and respect differing opinions. What Is This Course About? Welcome to World History. In this course we will seek an understanding of, well, the history of the world. Our goals will be to better appreciate the relevance of the past in our own lives, to learn about ourselves. Our study will be focused on the major civilizations in the world, though we will consider what is oft referred to as the Western World (the United States and Western Europe) less thoroughly than we look at the other parts of the globe. Primarily, we will consider those regions as a consequence of direct or indirect “contact” with the non-Western world, or as a result of major developments and/or alterations in the patterns of global exchange. In addition to learning the said content, we will also seek to improve writing, speaking, and critical and analytical thinking skills. World Population History (1 C.E. - 2050 C.E.)
|
|
World History: Patterns of Interaction
30 Must-See Historic Moments in Photographs
|
The photograph precipitated a dramatic change in how we perceive history. Amazing historic photos like these can make it seem like you were standing right there during that historic moment.
Books and paintings have documented history far further back, but there's nothing like a photo to give you the sense that you're looking at something real. A photo can still misdirect the viewer, but it's still more faithful than a painting or book. |
Ironic Lives of Two WWII Veterans
Little-known facts that almost never make it to history books.
The Histomap
The Entire History of the World—Really, All of It—Distilled Into a Single Gorgeous Chart
Click here to see a bigger, more clear version of the map.
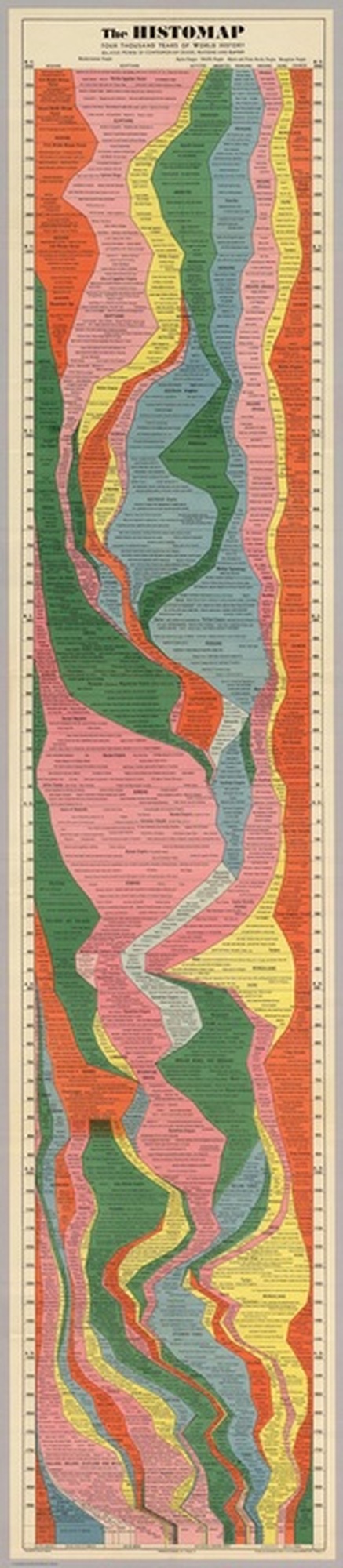
Four Thousand Years Of World History. Relative Power Of Contemporary States, Nations And Empires.
Copyright by John B. Sparks. Published by Histomap, Inc. Chicago, Ill.
Printed and distributed in the U.S.A. by Rand McNally & Co., Chicago, Ill.
Copyright by John B. Sparks. Published by Histomap, Inc. Chicago, Ill.
Printed and distributed in the U.S.A. by Rand McNally & Co., Chicago, Ill.



